二叉树
二叉树(Binary tree)是一种每个节点最多只有两个子节点的树类型的数据结构,通常将这两个节点称为左节点和右节点。 树和二叉树的主要区别在于:
- 树的节点个数至少为 1,而二叉树的节点个数可以为 0(二叉树允许是空树)
- 树中的最大度数(节点数量)没有限制,而二叉树的节点的最大度数为 2
- 树的节点没有左右之分,而二叉树的节点有左右之分
特征
- 若二叉树的层次从 0 开始,则在二叉树的第
i层至多有2^i个节点(i >= 0)i = 1时,只有一个根节点2^(i - 1) = 2^ 0 = 1
- 高度为
k的二叉树最多有2^(k + 1) - 1个节点(k>=-1)(空树的高度为-1)i = 2时,2 ^ (k + 1) - 1 = 2 ^ 3 - 1 = 7个节点
- 对任何一棵二叉树,如果其叶子节点(度为 0)数为
m,度为 2 的节点数为n, 则m = n + 1
特殊类型
二叉树也分为很多中类型。如满二叉树 或 完全二叉树。
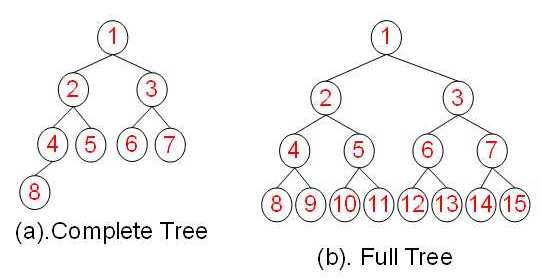
完全二叉树
- 概括:除了最后一层,其他层级都被填满,并且所有的节点都考左侧。
- 性质:
满二叉树
- 概括:所有层的节点都被完全填满。
- 性质:
- 叶节点的度为 0,其他节点的度为 2。
- 树的高度为 h, 则节点总数为 2^(h+1)-1
| 满二叉树 | 完全二叉树 | |
|---|---|---|
| 总节点 k | 2^(h - 1) <= k <= 2^h - 1 | k = 2^h - 1 |
| 树高 h | h = log2 k + 1 | h = log2(k + 1) |
二叉树搜索
二叉树的搜索主要分为 深度优先搜索(DFS) 和 广度优先搜索(BFS)两种方式。
深度优先搜索(DFS) 深度优先搜索(DFS)是一种用于遍历或搜索树或图的算法。在二叉树的上下文中,DFS 通常有三种主要的遍历方式:先序遍历、中序遍历和后序遍历。 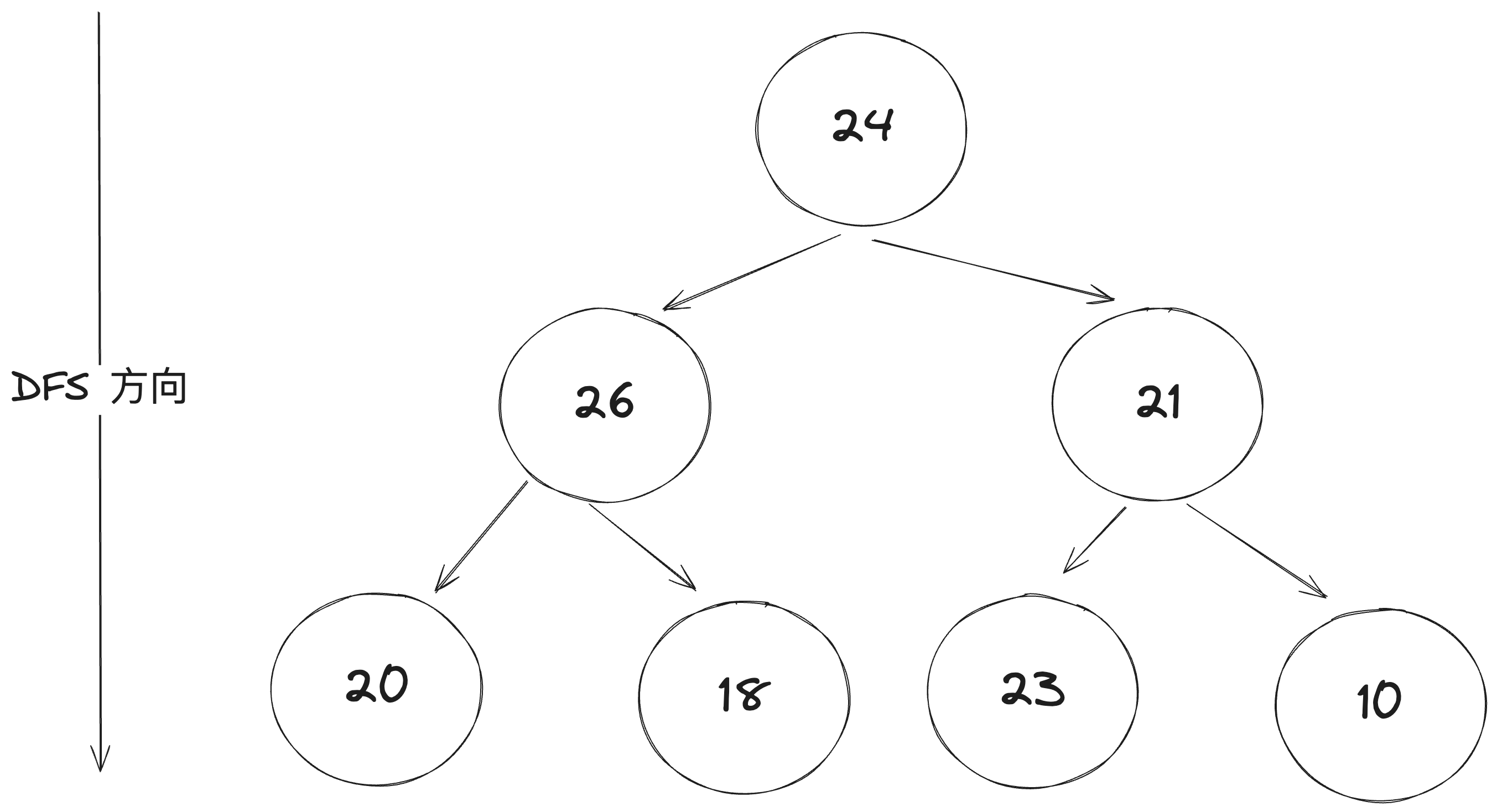
- 先序遍历:先访问根节点,然后遍历左子树,最后遍历右子树。
- 中序遍历:先遍历左子树,然后访问根节点,最后遍历右子树。对于二叉搜索树,中序遍历可以按升序访问所有节点。
- 后序遍历:先遍历左子树,然后遍历右子树,最后访问根节点。
广度优先搜索(BFS) 广度优先搜索(BFS)是从根节点开始,逐层遍历树中每个节点,同时每层从左到右遍历。BFS 通常使用队列来实现。
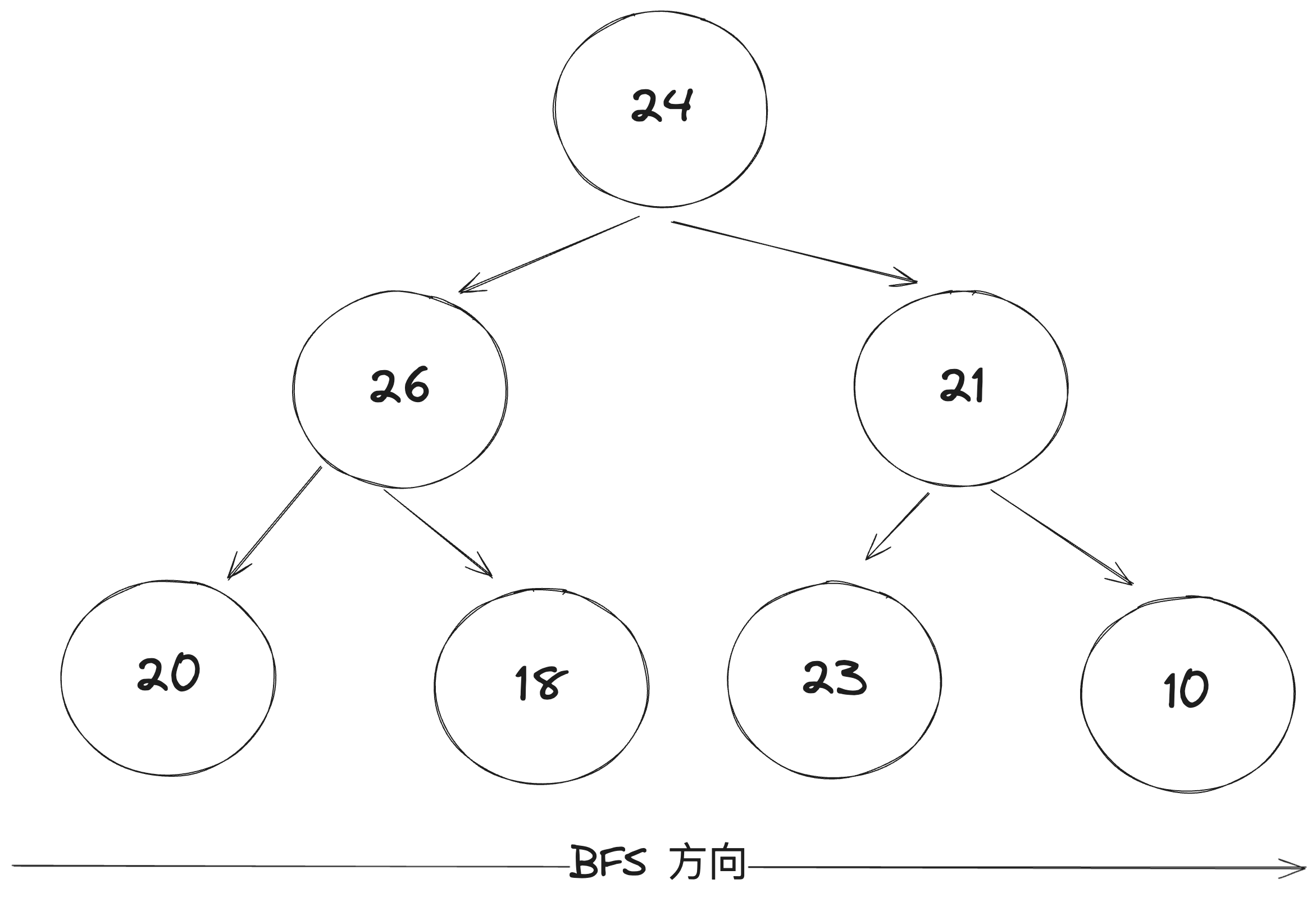
比较
- 时间效率:BFS 和 DFS 的时间复杂度很多时候是相同的,但在特定问题上,一种可能比另一种更高效。
- 空间效率:在实际应用中,DFS 通常比 BFS 占用更少的内存,因为 BFS 需要存储整个层的节点。
- 应用领域:BFS 更适合问题的最短路径(图)、层次遍历等场景,而 DFS 更适用于查找所有可能解的问题、深度优先的探索等。
前序遍历
先序遍历:先访问根节点,然后遍历左子树,最后遍历右子树。
ts
const preOrderTraversal = (root: BinaryTree) => {
const stack: BinaryTree[] = [];
const result: number[] = [];
let current: BinaryTree | null = root;
while (current || stack.length) {
while (current) {
result.push(current.value);
stack.push(current);
current = current.left;
}
current = stack.pop() || null;
current = current?.right || null;
}
return result;
};中序遍历
中序遍历:先遍历左子树,然后访问根节点,最后遍历右子树。对于二叉搜索树,中序遍历可以按升序访问所有节点。
ts
const inOrderTraversal = (root: BinaryTree) => {
const stack: BinaryTree[] = [];
const result: number[] = [];
let current: BinaryTree | null = root;
while (current || stack.length) {
while (current) {
stack.push(current);
current = current.left;
}
current = stack.pop()!;
result.push(current.value);
current = current.right;
}
return result;
};后序遍历
后序遍历:先遍历左子树,然后遍历右子树,最后访问根节点。
ts
import { BinaryTree } from "./binary-tree";
const postOrderTraversal = (root: BinaryTree) => {
const stack: BinaryTree[] = [root];
const result: number[] = [];
while (stack.length) {
const node = stack.pop()!;
result.unshift(node.value);
if (node.left) {
stack.push(node.left);
}
if (node.right) {
stack.push(node.right);
}
}
return result;
};
const a = new BinaryTree(2);
const b = new BinaryTree(3);
const c = new BinaryTree(4);
const b1 = new BinaryTree(6);
const b2 = new BinaryTree(5);
const c1 = new BinaryTree(7);
const c2 = new BinaryTree(8);
a.left = b;
a.right = c;
b.left = b1;
b.right = b2;
c.left = c1;
c.right = c2;
const res = postOrderTraversal(a);
console.log(res);层序遍历
广度优先搜索(BFS)是从根节点开始,逐层遍历树中每个节点,同时每层从左到右遍历。BFS 通常使用队列来实现。
ts
import { BinaryTree } from "./binary-tree";
const levelOrder = (root: BinaryTree) => {
const res: number[] = [];
const queue: BinaryTree[] = [root];
while (queue.length) {
const node = queue.shift()!;
res.push(node.value);
if (node.left) {
queue.push(node.left);
}
if (node.right) {
queue.push(node.right);
}
}
return res;
};
const a = new BinaryTree(2);
const b = new BinaryTree(3);
const c = new BinaryTree(4);
const b1 = new BinaryTree(6);
const b2 = new BinaryTree(5);
const c1 = new BinaryTree(7);
const c2 = new BinaryTree(8);
a.left = b;
a.right = c;
b.left = b1;
b.right = b2;
c.left = c1;
c.right = c2;
const res = levelOrder(a);
console.log(res);