二叉搜索树
定义
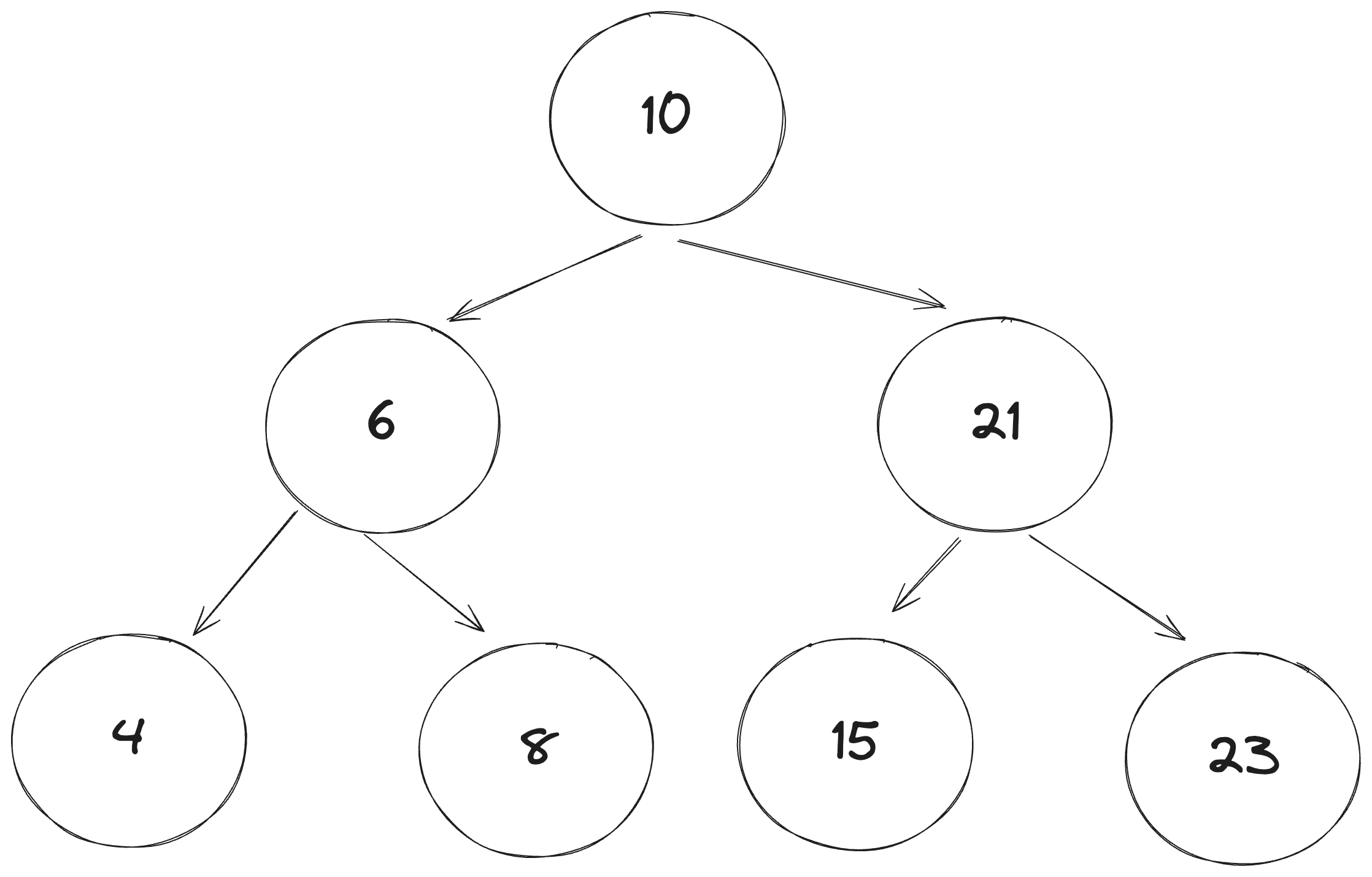
在计算机领域中,二叉搜索树(BST),也称为二叉搜索树、有序二叉树(ordered binary tree)或排序二叉树(sorted binary tree),是指一棵空树或者具有下列性质的二叉树
- 若任意节点的左子树不空,则左子树上所有节点的值均小于它的根节点的值;
- 若任意节点的右子树不空,则右子树上所有节点的值均大于它的根节点的值;
- 任意节点的左、右子树也分别为二叉查找树;
特性
访问、 插入、 删除 都是 `O(log(n)) 的时间复杂度。
| Access | Search | Insertion | Deletion |
|---|---|---|---|
| O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) |
操作
二叉搜索树支持多种操作,包括但不限于:
- 查找:搜索一个具有特定键的节点。
- 插入:插入一个具有特定键的新节点。
- 删除:删除一个具有特定键的节点。
- 遍历:按照某种顺序访问树中的每个节点,常见的遍历方式包括前序遍历、中序遍历和后序遍历。
查找操作
效率:由于二叉搜索树的性质,该函数的平均时间复杂度为 O(log n),其中 n 是树中节点的数量。这是因为每次比较都会将搜索空间减半。 在最坏的情况下(树高度等于节点数,即树完全倾斜时),时间复杂度为 O(n)。
ts
import { BinarySearchTree } from ".";
const findNode = (root: BinarySearchTree, value: number) => {
if (!root) {
return null;
}
let currentNode: BinarySearchTree | null = root;
while (currentNode) {
if (currentNode.value === value) {
return currentNode;
}
if (currentNode.value > value) {
currentNode = currentNode.left;
} else {
currentNode = currentNode.right;
}
}
return null;
};
const a = new BinarySearchTree(10);
const b = new BinarySearchTree(6);
const c = new BinarySearchTree(21);
const b1 = new BinarySearchTree(4);
const b2 = new BinarySearchTree(8);
const c1 = new BinarySearchTree(15);
const c2 = new BinarySearchTree(23);
a.left = b;
a.right = c;
b.left = b1;
b.right = b2;
c.left = c1;
c.right = c2;
const node = findNode(a, 21);
console.log("node1", node);
const node2 = findNode(a, 0);
console.log("node2", node2);插入操作
效率: 与查找操作相似,插入操作的平均时间复杂度也是 O(log n),但在最坏的情况下(树完全倾斜)时间复杂度是 O(n)。
ts
import { BinarySearchTree } from ".";
const insertNode = (root: BinarySearchTree, value: number): boolean => {
if (!root) {
return false;
}
let currentNode: BinarySearchTree | null = root;
while (currentNode) {
if (currentNode.value === value) {
return false;
}
if (currentNode.value > value) {
if (!currentNode.left) {
currentNode.left = new BinarySearchTree(value);
return true;
} else {
currentNode = currentNode.left;
}
continue;
}
if (currentNode.value < value) {
if (!currentNode.right) {
currentNode.right = new BinarySearchTree(value);
return true;
} else {
currentNode = currentNode.right;
}
continue;
}
}
return false;
};
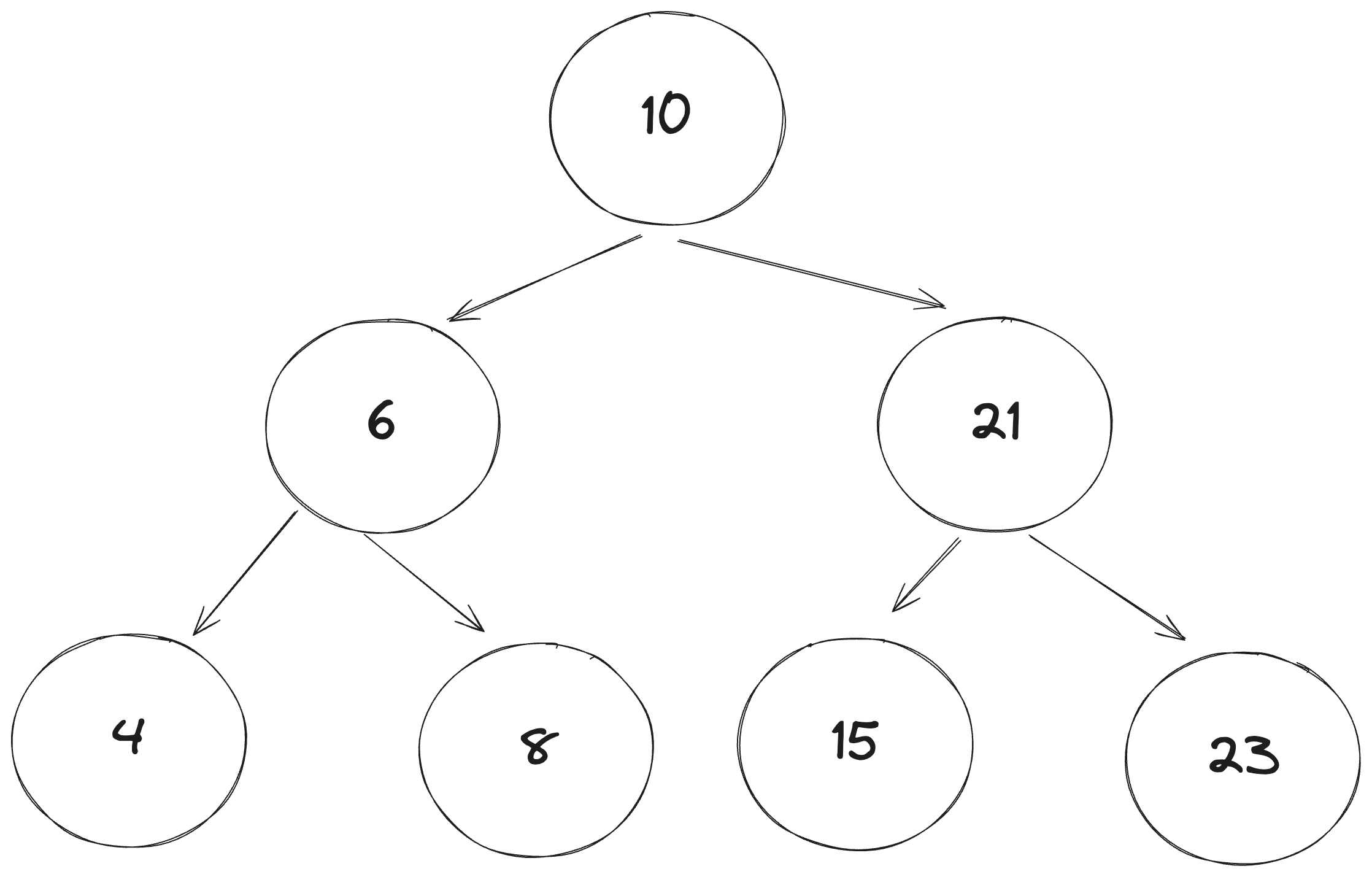
const a = new BinarySearchTree(10);
const b = new BinarySearchTree(6);
const c = new BinarySearchTree(21);
const b1 = new BinarySearchTree(4);
const b2 = new BinarySearchTree(8);
const c1 = new BinarySearchTree(15);
const c2 = new BinarySearchTree(23);
a.left = b;
a.right = c;
b.left = b1;
b.right = b2;
c.left = c1;
c.right = c2;
const result = insertNode(a, 17);
console.log("node1", result, JSON.stringify(a, null, 2));删除操作
删除的逻辑比较复杂,下方才用了迭代来进行处理。
ts
import { BinarySearchTree } from ".";
const getSmallest = (node: BinarySearchTree): BinarySearchTree => {
if (node.left === null) {
return node;
} else {
return getSmallest(node.left);
}
};
const deleteNode = (
root: BinarySearchTree | null,
value: number
): BinarySearchTree | null => {
if (!root) {
return null;
}
if (root.value === value) {
if (root.left === null && root.right === null) {
return null;
}
if (root.left === null) {
return root.right;
}
if (root.right === null) {
return root.left;
}
// 待删除节点有两个子节点
// 需要找到待删除节点左子树中的最小值
const minNode = getSmallest(root.right);
// 将右子树最小值赋值给待删除节点
root.value = minNode.value;
// 删除右子树刚才找到的最小值的节点
root.right = deleteNode(root.right, minNode.value);
} else if (value < root.value) {
root.left = deleteNode(root.left, value);
} else {
root.right = deleteNode(root.right, value);
}
return root;
};
const a = new BinarySearchTree(10);
const b = new BinarySearchTree(6);
const c = new BinarySearchTree(21);
const b1 = new BinarySearchTree(4);
const b2 = new BinarySearchTree(8);
const c1 = new BinarySearchTree(15);
const c2 = new BinarySearchTree(23);
a.left = b;
a.right = c;
b.left = b1;
b.right = b2;
c.left = c1;
c.right = c2;
const result = deleteNode(a, 21);
console.log("node1", JSON.stringify(result, null, 2));遍历操作
遍历和二叉树的遍历逻辑是一样的。但注意,如果是中序遍历,则整体会变成一个升序排序。 举个例子:4、6、8、10、15、21、23