图
图是由节点和节点之间的边组成的集合。
在计算机科学中,图(英語:graph)是一种抽象数据类型,用于实现数学中图论的无向图和有向图的概念。
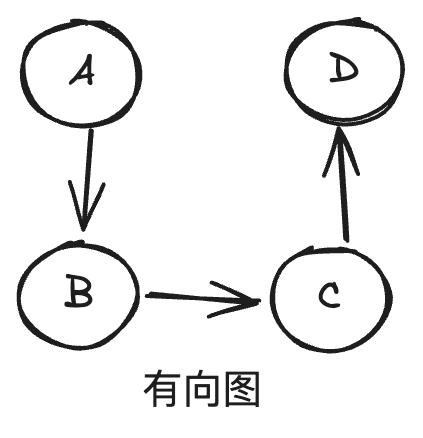
图的数据结构包含一个有限(可能是可变的)的集合作为节点集合,以及一个无序对(对应无向图)或有序对(对应有向图)的集合作为边(有向图中也称作弧)的集合。节点可以是图结构的一部分,也可以是用整数下标或引用表示的外部实体。 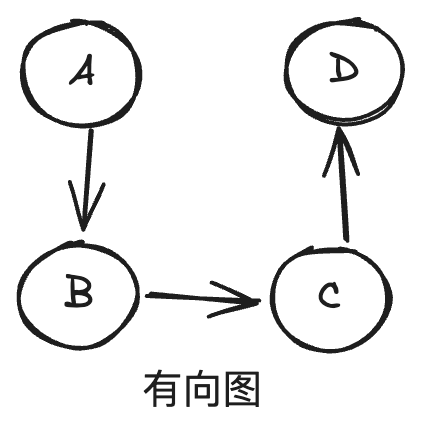
图的数据结构还可能包含和每条边相关联的数值(edge value),例如一个标号或一个数值(即权重,weight;表示花费、容量、长度等)。
基本概念
- 顶点(Vertex):图中的一个节点。
- 边(Edge):连接图中的两个顶点,可以是有向的也可以是无向的。
- 度(Degree):一个顶点拥有的边数。对于有向图,「入度 in-degree」表示有多少条边指向该顶点,「出度 out-degree」表示有多少条边从该顶点指出。
- 路径:顶点的一个序列,其中任意两个连续的顶点都通过图中的一条边连接。
- 连通图:在无向图中,如果任意两个顶点间都存在路径,则该图为连通图。
- 强连通图:在有向图中,如果任意两个顶点间都存在路径,则该图为强连通图。
- 图的遍历:指的是按照某种顺序访问图中所有顶点的过程。主要的遍历算法有深度优先搜索(DFS)和广度优先搜索(BFS)。
分类
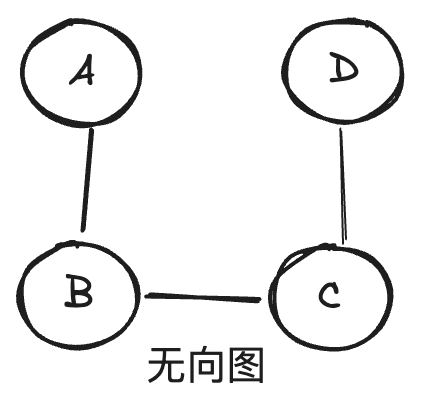
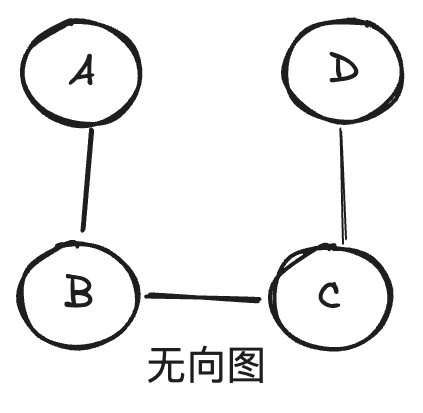
- 无向图:边没有方向,表示节点间的关系是双向的或者说是对等的。
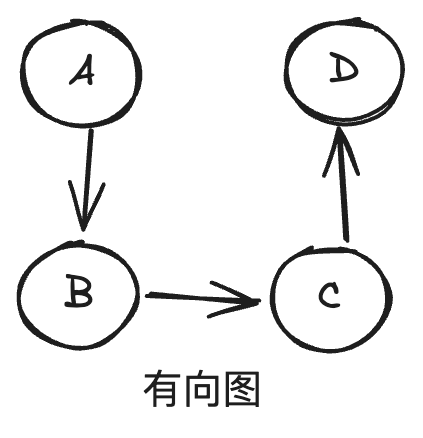
- 有向图:边有方向,表示从一个节点到另一个节点的单向关系。
- 加权图:边上带有权重,表示节点间关系的某种度量(如成本、距离等)。
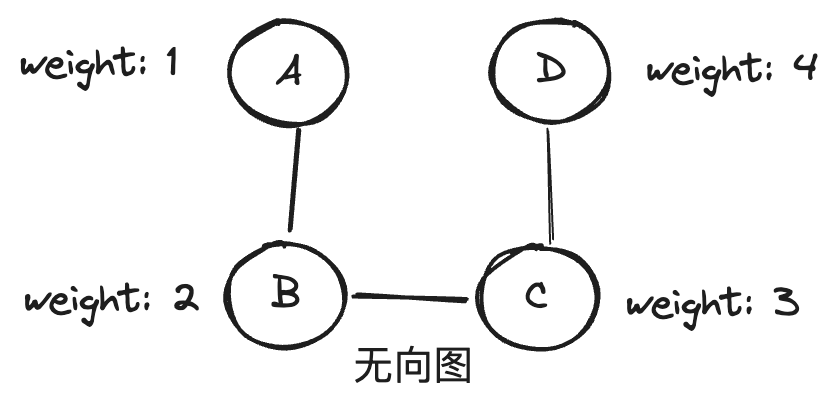
- 非加权图:边上没有权重,仅表示节点间存在关系。
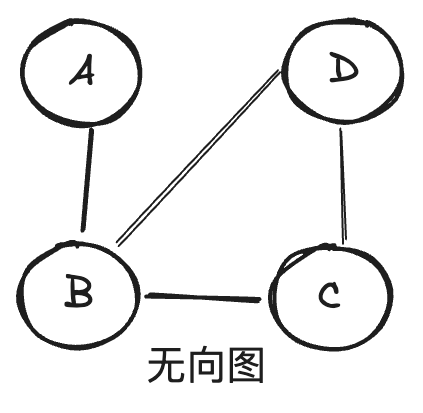
- 带环图:图中存在环状结构。
图的表示
图主要有两种表示方法:邻接矩阵和邻接表。
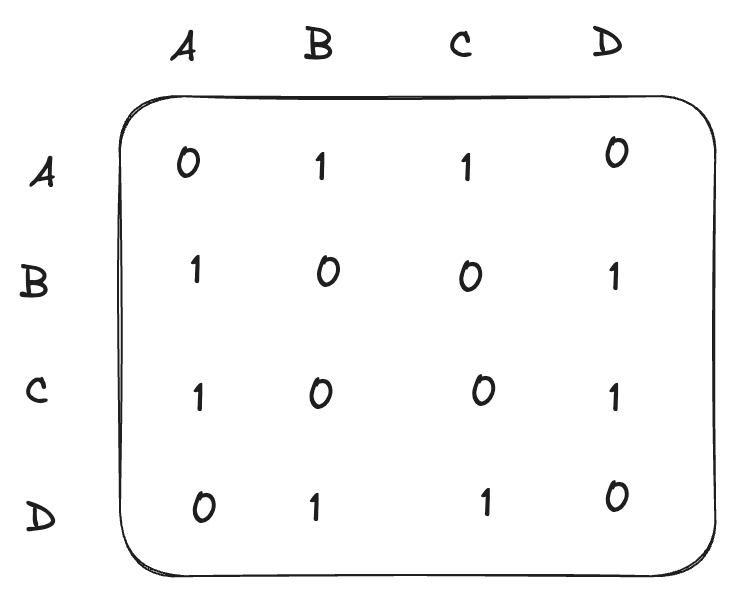
- 邻接矩阵:使用二维数组来表示图中顶点之间的连接关系。对于无向图来说,邻接矩阵是对称的。这种表示方法空间复杂度较高,但是可以快速查询任意两个顶点是否相连。
ts
class Graph {
private matrix: number[][];
private vertices: string[];
private verticesIndex: Map<string, number>;
constructor(vertexCount: number) {
this.matrix = new Array(vertexCount)
.fill(null)
.map(() => new Array(vertexCount).fill(0));
this.vertices = [];
this.verticesIndex = new Map<string, number>();
}
addVertex(vertex: string) {
if (this.verticesIndex.has(vertex)) {
return;
}
const index = this.vertices.length;
this.vertices.push(vertex);
this.verticesIndex.set(vertex, index);
}
addEdge(v1: string, v2: string, weight = 1) {
const index1 = this.verticesIndex.get(v1);
const index2 = this.verticesIndex.get(v2);
if (index1 === undefined || index2 === undefined) {
return;
}
this.matrix[index1][index2] = weight;
this.matrix[index2][index1] = weight;
}
hasEdge(v1: string, v2: string) {
const index1 = this.verticesIndex.get(v1);
const index2 = this.verticesIndex.get(v2);
if (index1 === undefined || index2 === undefined) {
return false;
}
return this.matrix[index1][index2] !== 0;
}
print() {
console.log(this.matrix);
}
}
// 使用示例
const graph = new Graph(4);
graph.addVertex("A");
graph.addVertex("B");
graph.addVertex("C");
graph.addVertex("D");
graph.addEdge("A", "B");
graph.addEdge("B", "C");
graph.addEdge("C", "D");
graph.addEdge("D", "A");
graph.print();- 邻接表:为每个顶点维护一个列表,列出直接连接到的所有顶点。这种表示方法更加节省空间,尤其是对于稀疏图。
ts
type Vertex = string;
type Edge = { vertex: Vertex; weight: number };
type AdjacencyList = Map<Vertex, Edge[]>;
class WeightedGraph {
private adjacencyList: AdjacencyList;
constructor() {
this.adjacencyList = new Map<Vertex, Edge[]>();
}
addVertex(vertex: Vertex): void {
if (this.adjacencyList.get(vertex)) {
return;
}
this.adjacencyList.set(vertex, []);
}
addEdge(vertex1: Vertex, vertex2: Vertex, weight = 1) {
if (!this.adjacencyList.get(vertex1) || !this.adjacencyList.get(vertex2)) {
return;
}
this.adjacencyList.get(vertex1)?.push({
vertex: vertex2,
weight,
});
this.adjacencyList.get(vertex2)?.push({
vertex: vertex1,
weight,
});
}
print() {
for (let [vertex, edges] of this.adjacencyList) {
const edgeStr = edges
.map((edge) => `${edge.vertex} (${edge.weight})`)
.join(", ");
console.log(`${vertex} -> ${edgeStr}`);
}
}
}
const graph2 = new WeightedGraph();
graph2.addVertex("A");
graph2.addVertex("B");
graph2.addVertex("C");
graph2.addEdge("A", "B", 1);
graph2.addEdge("A", "C", 2);
graph2.addEdge("B", "C", 3);
graph2.print();综合来看,邻接矩阵体现了“以空间换时间”的原则,而邻接表体现了“以时间换空间”的原则。
图的遍历
- 深度优先搜索(DFS):模仿走迷宫,尽可能深地搜索图的分支。
- 广度优先搜索(BFS):从源顶点开始,逐层遍历图,先访问离源顶点最近的顶点。
整体代码
领接数组
ts
class Graph {
private matrix: number[][];
private vertices: string[];
private verticesIndex: Map<string, number>;
constructor(vertexCount: number) {
this.matrix = new Array(vertexCount)
.fill(null)
.map(() => new Array(vertexCount).fill(0));
this.vertices = [];
this.verticesIndex = new Map<string, number>();
}
addVertex(vertex: string) {
if (this.verticesIndex.has(vertex)) {
return;
}
const index = this.vertices.length;
this.vertices.push(vertex);
this.verticesIndex.set(vertex, index);
}
addEdge(v1: string, v2: string, weight = 1) {
const index1 = this.verticesIndex.get(v1);
const index2 = this.verticesIndex.get(v2);
if (index1 === undefined || index2 === undefined) {
return;
}
this.matrix[index1][index2] = weight;
this.matrix[index2][index1] = weight;
}
hasEdge(v1: string, v2: string) {
const index1 = this.verticesIndex.get(v1);
const index2 = this.verticesIndex.get(v2);
if (index1 === undefined || index2 === undefined) {
return false;
}
return this.matrix[index1][index2] !== 0;
}
print() {
console.log(this.matrix);
}
BFS(startVertex: string): void {
const startVertexIndex = this.verticesIndex.get(startVertex);
if (startVertexIndex === undefined) {
return;
}
const queue: number[] = [];
const visited: boolean[] = [];
queue.push(startVertexIndex);
visited[startVertexIndex] = true;
while (queue.length) {
const currentIndex = queue.shift()!;
console.log(`${this.vertices[currentIndex]} `);
const targetMatrix = this.matrix[currentIndex] || [];
for (let i = 0; i < targetMatrix.length; i++) {
if (targetMatrix[i] && !visited[i]) {
visited[i] = true;
queue.push(i);
}
}
}
}
DFS(startVertex: string): void {
const visited = new Array(this.vertices.length).fill(false);
const DFSUtils = (idx: number) => {
visited[idx] = true;
console.log(this.vertices[idx]);
for (let i = 0; i < this.matrix[idx].length; i++) {
if (this.matrix[idx][i] && !visited[i]) {
DFSUtils(i);
}
}
};
const startIdx = this.verticesIndex.get(startVertex);
if (startIdx !== undefined) {
DFSUtils(startIdx);
}
}
}
// 使用示例
const graph = new Graph(4);
graph.addVertex("A");
graph.addVertex("B");
graph.addVertex("C");
graph.addVertex("D");
graph.addEdge("A", "B");
graph.addEdge("B", "C");
graph.addEdge("C", "D");
graph.addEdge("D", "A");
graph.print();
console.log("BFS: ");
graph.BFS("A");
console.log("\nDFS: ");
graph.DFS("A");领接表
ts
type Vertex = string;
type Edge = { vertex: Vertex; weight: number };
type AdjacencyList = Map<Vertex, Edge[]>;
class WeightedGraph {
private adjacencyList: AdjacencyList;
constructor() {
this.adjacencyList = new Map<Vertex, Edge[]>();
}
addVertex(vertex: Vertex): void {
if (this.adjacencyList.get(vertex)) {
return;
}
this.adjacencyList.set(vertex, []);
}
addEdge(vertex1: Vertex, vertex2: Vertex, weight = 1) {
if (!this.adjacencyList.get(vertex1) || !this.adjacencyList.get(vertex2)) {
return;
}
this.adjacencyList.get(vertex1)?.push({
vertex: vertex2,
weight,
});
this.adjacencyList.get(vertex2)?.push({
vertex: vertex1,
weight,
});
}
print() {
for (let [vertex, edges] of this.adjacencyList) {
const edgeStr = edges
.map((edge) => `${edge.vertex} (${edge.weight})`)
.join(", ");
console.log(`${vertex} -> ${edgeStr}`);
}
}
BFS(vertex: Vertex) {
const visited: Record<Vertex, boolean> = {};
const queue: Vertex[] = [vertex];
visited[vertex] = true;
while (queue.length) {
const currentVertex = queue.shift()!;
console.log(`${currentVertex} `);
const edge = this.adjacencyList.get(currentVertex);
if (edge) {
for (let i = 0; i < edge.length; i++) {
const { vertex } = edge[i];
if (vertex && !visited[vertex]) {
queue.push(vertex);
visited[vertex] = true;
}
}
}
}
}
DFS(vertex: Vertex) {
const visited: Record<Vertex, boolean> = {};
const DFSUtils = (targetVertex: Vertex) => {
console.log(`${targetVertex} `);
visited[targetVertex] = true;
const edges = this.adjacencyList.get(targetVertex);
if (edges) {
for (let i = 0; i < edges.length; i++) {
const { vertex: nextVertex } = edges[i];
if (nextVertex && !visited[nextVertex]) {
DFSUtils(nextVertex);
}
}
}
};
DFSUtils(vertex);
}
}
const graph2 = new WeightedGraph();
graph2.addVertex("A");
graph2.addVertex("B");
graph2.addVertex("C");
graph2.addVertex("D");
graph2.addEdge("A", "B", 1);
graph2.addEdge("A", "C", 2);
graph2.addEdge("B", "D", 2);
graph2.addEdge("B", "C", 3);
graph2.print();
console.log("BFS:");
graph2.BFS("A");
console.log("DFS:");
graph2.DFS("A");