哈希表
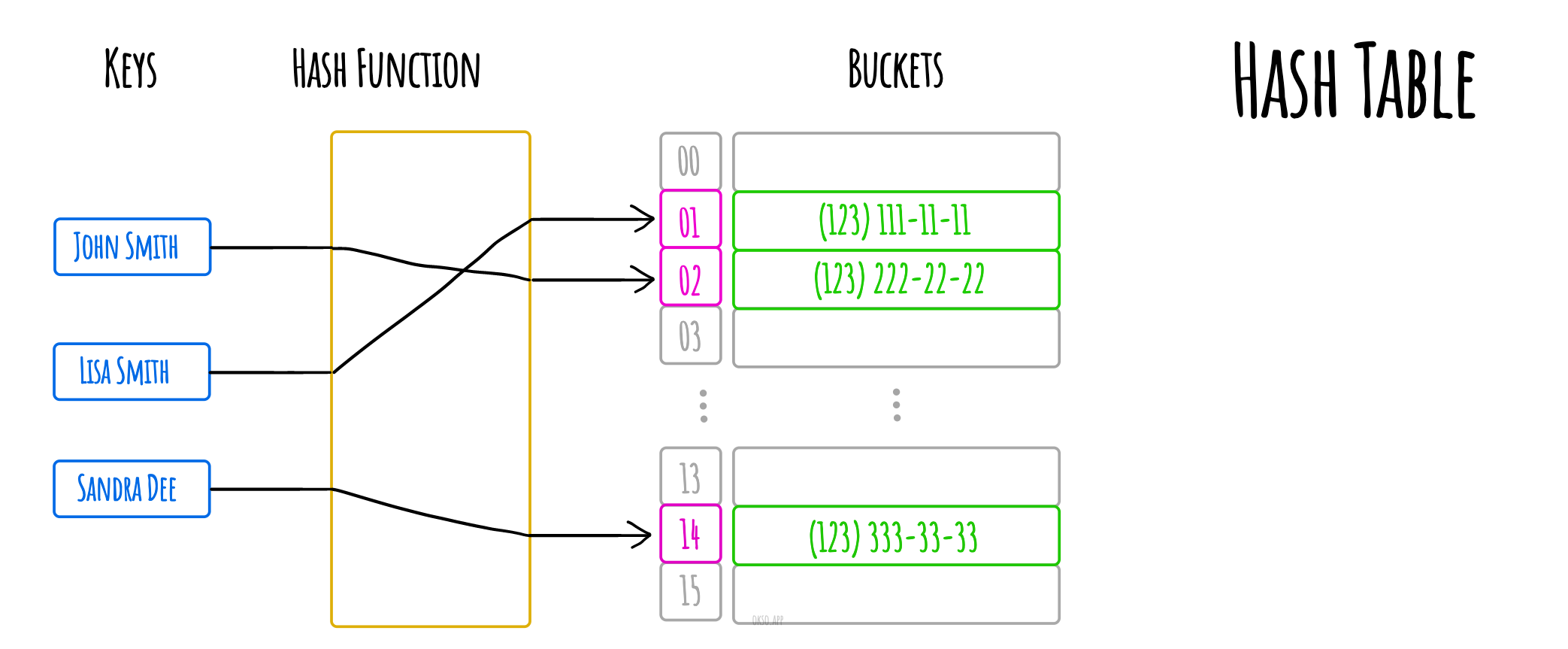
在计算机领域的定义中,哈希表(hash map or hash table)是一种实现关联数组(associative array)的抽象数据类型,该结构可以将键(key)映射成值(value)。
关联数组,也被称为映射(Map)或字典(Dictionary),是一种允许我们使用键(Key)而不是数字索引来存储和访问数据的数据结构。
- 关联:根据 key 能关联(映射)value。
- 数组:底层还是基于数组做数据存储,但可以通过一些规则(如哈希表通过哈希函数)将 key -> 索引,从而根据索引去找数组中具体的值。
哈希表使用 哈希函数/散列函数 来计算一个值在数组或桶(buckets)中或槽(slots)中对应的索引,可使用该索引找到所需的值。
理想情况下,哈希函数会给每一个键有唯一的桶,但是大多数的哈希表设计采用不完美的散列函数,可能会导致“哈希冲突”,也就是散列函数为多个键(key)生成了相同的索引,这种碰撞必须以某种方式进行处理。
哈希函数
哈希函数,又称散列函数能使对一个数据序列的访问过程更加迅速有效,通过散列函数,数据元素将被更快定位。
主要特性
- 确定性:同一个输入数据每次通过哈希函数得到的哈希值都是相同的。
- 高效性:哈希函数对数据的处理速度应当快速,能够迅速返回哈希值。
- 随机分布性:对于输入数据的微小改动,产生的哈希值应该有很大的不同,这被称为雪崩效应。
- 不可逆性:从哈希值不应能够直接反推出原始数据(单向性)。
常见的哈希函数
哈希函数的种类很多,有哈希函数有很多种,它们各自适用于不同的应用场景。以下是一些常见的哈希函数:
除法哈希(Division Hashing): 这种函数通过取关键字与哈希表大小的模(余数)来分配索引,即
h(k) = k mod m,其中k是关键字,m是表大小。乘法哈希(Multiplication Hashing): 这里,关键字乘以一个常数,取结果的分数部分,并乘以表的大小,最后取整。公式如
h(k) = floor(m * (k * A mod 1)),A是 0 和 1 之间的常数。通用哈希(Universal Hashing): 随机选取哈希函数的系列,以此来减少哈希碰撞的几率。
平方取中哈希: 关键字平方后取中间几位作为哈希值,以尽量避免碰撞。
具体的哈希函数设计,取决于你的具体场景。
哈希冲突
哈希冲突(Hash Collision)是指两个不同的输入数据(或称为键)在使用同一个哈希函数处理后得到相同的哈希值的情况。由于哈希函数是将一个较大(通常是无限的)输入域映射到一个较小(通常是有限的)输出域,因此根据鸽巢原理,在足够多的输入或特定的条件下,必然会出现至少两个不同的输入得到相同输出的情况。
具体例子
具体来说,考虑一个哈希函数 h,它将输入空间 I 映射到输出空间 O。如果存在两个不同的输入 x 和 y(x ≠ y),使得 h(x) = h(y),那么我们就说发生了一个哈希冲突。
注意:哈希函数本身并不解决哈希冲突。
哈希冲突的示例:考虑一个简单的哈希函数 h(k) = k mod 10,并且有两个不同的键 k1 = 12 和 k2 = 22。当应用哈希函数 h 到 k1 和 k2 上时,得到:
h(12) = 12 mod 10 = 2h(22) = 22 mod 10 = 2在这个例子中,k1 和 k2 发生了哈希冲突,因为它们具有相同的哈希值 2。
解决策略
在哈希表的实现中,冲突解决策略是必须的,以确保每个输入值都能够被正确处理。以下是一些常见的冲突解决方法:
开放寻址(Open Addressing):如果产生了冲突,就按某种系统的方式探查哈希表的其他位置来找到空位。
链表法(Chaining):在哈希表的每个槽位上维护一个链表,所有具有相同哈希值的输入项都存储在相同槽位的链表中。
双重散列(Double Hashing):使用一组哈希函数而不是单一哈希函数,在发生冲突时使用另一个哈希函数来确定探查序列。
再哈希(Rehashing):当哈希表变得过于拥挤时(即装填因子变大),使用一个新的哈希函数和更大的哈希表大小进行再哈希,以减少冲突并重新分配已有的项。
代码实现
下方我们用 TS 结合数组的数据结构来进行哈希表的具体实现吧。
哈希函数计算
注意,哈希函数的作用是将输入(即键)映射到一个整数,这个整数作为数组(哈希表)的索引。不解决具体冲突。 同时,哈希函数的算法并不固定,取决于具体场景,具体实现。
下方是一种实现方式,无需关注具体细节,只需要记住将 key -> index 即可。
class HashTable<K, V> {
private table: Array<Array<[K, V]>>;
private size: number; // 哈希表大小
private hash(key: K): number {
const stringKey = JSON.stringify(key);
let hash = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < stringKey.length; i++) {
const char = stringKey.charCodeAt(i);
hash = (hash << 5) - hash + char;
hash = hash & hash; // Convert to 32bit integer
}
return Math.abs(hash) % this.size;
}
}解决哈希冲突
哈希函数计算完,会得到一个索引,我们将索引和桶进行关联,在桶中去做存储键值对和解决哈希冲突。 具体来说,我们每一个桶是是 [key, value] 的数组。 通过数组天然提供的 find、findIndex 属性,我们能在确保在哈希冲突的情况下,我们通过其他信息,如 key 来进行 get、put、remove 的操作。
class HashTable<K, V> {
private table: Array<Array<[K, V]>>;
private size: number; // 哈希表大小
constructor(size: number = 100) {
this.size = size;
this.table = new Array(size);
for (let i = 0; i < size; i++) {
this.table[i] = [];
}
}
put(key: K, value: V): void {
const index = this.hash(key);
const bucket = this.table[index];
const foundIndex = bucket.findIndex((item) => item[0] === key);
if (foundIndex !== -1) {
bucket[foundIndex][1] = value;
} else {
bucket.push([key, value]);
}
}
get(key: K): V | undefined {
const index = this.hash(key);
const bucket = this.table[index];
const target = bucket.find((item) => item[0] === key);
return target ? target[1] : undefined;
}
}整体代码
class HashTable<K, V> {
private table: Array<Array<[K, V]>>;
private size: number; // 哈希表大小
constructor(size: number = 100) {
this.size = size;
this.table = new Array(size);
for (let i = 0; i < size; i++) {
this.table[i] = [];
}
}
private hash(key: K): number {
const stringKey = JSON.stringify(key);
let hash = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < stringKey.length; i++) {
const char = stringKey.charCodeAt(i);
hash = (hash << 5) - hash + char;
hash = hash & hash; // Convert to 32bit integer
}
return Math.abs(hash) % this.size;
}
put(key: K, value: V): void {
const index = this.hash(key);
const bucket = this.table[index];
const foundIndex = bucket.findIndex((item) => item[0] === key);
if (foundIndex !== -1) {
bucket[foundIndex][1] = value;
} else {
bucket.push([key, value]);
}
}
get(key: K): V | undefined {
const index = this.hash(key);
const bucket = this.table[index];
const target = bucket.find((item) => item[0] === key);
return target ? target[1] : undefined;
}
remove(key: K): boolean {
const index = this.hash(key);
const bucket = this.table[index];
const foundIndex = bucket.findIndex((item) => item[0] === key);
if (foundIndex === -1) {
return false;
}
bucket.splice(foundIndex, 1);
return true;
}
}